
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
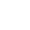
What is a Motion Sensor IC?
A motion sensor is an electronic device designed to detect physical movement within its operational vicinity. It serves as a crucial component in various systems, enabling them to respond to the presence or movement of objects, whether they are living beings like humans and animals or inanimate objects in motion. By converting the detected motion into an electrical signal, motion sensors communicate the occurrence of movement to other connected devices or systems, triggering specific actions or alerts. This functionality makes motion sensors invaluable in applications ranging from security and automation to energy management, bridging the gap between the physical world's dynamic changes and the digital systems that control and monitor our environments. https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
How do Motion Sensors Work?
Motion sensors operate on the principle of detecting changes in their surroundings and translating those changes into actionable information. At their core, they rely on various physical phenomena and technologies to sense motion. When an object moves within the sensor's field of view, it causes a disruption in a particular measurable quantity, such as infrared radiation, electromagnetic fields, or sound waves. The sensor is equipped with a sensing element that is highly sensitive to these changes. Once the sensing element detects a change, it generates an electrical signal, which is then processed by an internal circuit. This circuit analyzes the signal to determine if it meets the predefined criteria for motion detection. If the criteria are satisfied, the sensor sends an output signal to an external device, such as an alarm system, lighting controller, or security camera, initiating the appropriate response.
Understanding Motion Sensor Technology https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Passive Infrared (PIR) Technology
PIR sensors are based on the detection of infrared (IR) radiation emitted by objects. All objects with a temperature above absolute zero radiate IR energy, and human bodies, being warmer than their surroundings, emit a significant amount of it. A PIR sensor contains a pyroelectric sensor with two slots made of a material sensitive to IR radiation. When a warm object, like a person, enters the sensor's field of view, the IR radiation detected by the two slots changes differentially. This differential change creates a pulse of electrical current, which the sensor interprets as motion. A Fresnel lens is often incorporated with PIR sensors. This lens focuses the incoming IR radiation onto the sensing element, expanding the sensor's detection area and improving its sensitivity.
Microwave Technology
Microwave motion sensors utilize continuous waves of microwave radiation, similar to how radar systems operate. These sensors emit high-frequency radio waves into their surroundings. When an object moves within the range of these waves, it reflects the microwaves back to the sensor. The sensor then measures the frequency shift of the reflected waves, known as the Doppler effect. If the detected frequency shift exceeds a certain threshold, it indicates the presence of motion, and the sensor activates. Microwave sensors can penetrate certain materials, allowing them to detect movement behind non-metallic barriers, but this characteristic can also lead to false alarms in some cases.
Ultrasonic Technology
Ultrasonic motion sensors work by emitting high-frequency sound waves, typically above the range of human hearing (20 kHz and above). These sound waves travel through the air and bounce off objects in their path. When an object moves, the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel to the object and back to the sensor (the time-of-flight) changes. The sensor measures this time difference and calculates the distance to the object. By continuously monitoring these distance changes, the sensor can detect motion. Ultrasonic sensors are effective for detecting movement in open spaces and can work well in various lighting conditions, as they are not affected by light or darkness.
Dual Tech/Hybrid Technology
Dual tech or hybrid motion sensors combine two or more sensing technologies, usually PIR and microwave, to reduce false alarms. Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses, and by integrating them, the sensor can provide more reliable motion detection. For example, a sudden change in temperature might trigger a PIR sensor, while wind or vibrations could cause a microwave sensor to false alarm. In a dual tech sensor, both the PIR and microwave components must detect a change simultaneously for the sensor to be activated, significantly minimizing the occurrence of false positives.
Types of Motion Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors
As mentioned earlier, PIR sensors are among the most commonly used motion sensors due to their low cost, simplicity, and relatively low power consumption. They are widely employed in residential and commercial settings for applications such as automatic lighting control, security alarms, and occupancy detection in rooms. Their compact size and ease of installation make them a popular choice for DIY projects as well.
Microwave Sensors
Microwave sensors offer a larger detection range compared to PIR sensors and can work effectively in outdoor environments or large indoor spaces. They are often used in industrial settings, parking lots, and large warehouses where broad coverage is required. However, their higher cost and susceptibility to interference limit their use in some sensitive applications.
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors are suitable for applications where precise distance measurement in addition to motion detection is needed. They are commonly found in automatic door systems, robotic navigation, and industrial automation, where they can detect the approach of objects and determine their distance accurately. Their ability to function in various weather conditions also makes them useful for outdoor applications.
Dual Tech/Hybrid Sensors
Dual tech sensors are designed for high-security applications where minimizing false alarms is crucial. They are frequently installed in banks, government buildings, and other sensitive facilities. Their enhanced reliability makes them a preferred choice when false alarms could have serious consequences, such as unnecessary evacuations or security breaches.
Active Infrared (AIR) Sensors
AIR sensors consist of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a beam of infrared light, and the receiver detects the light. When an object breaks the beam, it interrupts the flow of infrared light to the receiver, triggering the sensor. These sensors are often used in perimeter security systems, where they can create an invisible barrier to detect intruders crossing a specific boundary.
What are the Most Common Applications that Motion Sensors are Used in? https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Security Systems
Motion sensors are a cornerstone of modern security systems. In residential homes, they are integrated into burglar alarms, detecting the movement of unauthorized individuals and triggering an audible alarm, sending alerts to homeowners' smartphones, or notifying security monitoring services. In commercial buildings, motion sensors are used to protect valuable assets, restrict access to sensitive areas, and monitor for suspicious activity. They can also be paired with security cameras, causing the cameras to start recording when motion is detected, providing valuable evidence in case of a break-in.
Lighting Control
One of the most widespread applications of motion sensors is in lighting systems. In offices, schools, and public restrooms, motion-activated lights automatically turn on when someone enters the room and turn off after a period of inactivity. This not only saves energy by eliminating the need for lights to remain on when no one is present but also provides convenience, as users don't have to fumble for light switches in the dark. In outdoor settings, motion sensor lights are used to illuminate walkways, driveways, and gardens, enhancing safety and security while reducing electricity consumption.
Home Automation
Motion sensors play a vital role in smart home ecosystems. They can be integrated with other smart devices, such as thermostats, smart locks, and home assistants. For example, when a motion sensor detects that a person has entered a room, it can send a signal to adjust the thermostat to a comfortable temperature, unlock the door, or turn on the television. In smart gardens, motion sensors can trigger automatic watering systems when plants need attention or activate sprinklers to deter animals from entering the garden.
Industrial Automation
In industrial environments, motion sensors are used for various purposes. They are employed in manufacturing processes to monitor the movement of conveyor belts, detect the presence of parts, and ensure the proper functioning of machinery. In robotic systems, motion sensors help robots navigate their surroundings, avoid obstacles, and interact with objects accurately. Additionally, motion sensors are used in quality control processes to detect any abnormal movement or vibrations in equipment, indicating potential malfunctions before they cause major breakdowns.
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, motion sensors are used to monitor patients, especially those who are elderly or have mobility issues. Wearable motion sensors can track a patient's movement patterns, detect falls, and alert caregivers in case of an emergency. In hospitals, motion sensors are also used to monitor the occupancy of rooms, ensuring that beds are available when needed and optimizing the use of hospital resources.
Is there a Difference between Motion Sensors and Detectors?
In common usage, the terms "motion sensor" and "motion detector" are often used interchangeably, and they generally refer to devices that are designed to sense the movement of objects. However, some might argue that a "sensor" is more focused on the physical component that detects the change in the environment (such as the sensing element in a PIR sensor), while a "detector" implies a more complete device that includes the sensing element along with the processing and output components that actually determine if motion has occurred and trigger an action. But in practice, the distinction is not widely recognized, and both terms are used to describe the overall device that performs the function of motion detection.
Why do I Need a Motion Sensor? https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Energy Savings
Motion sensors contribute significantly to energy conservation. By automatically turning off lights, appliances, or heating/cooling systems when no one is present in a room, they prevent unnecessary energy consumption. This not only reduces electricity bills but also helps in minimizing the environmental impact by decreasing energy waste.
Enhanced Security
Motion sensors act as a powerful deterrent to burglars and intruders. Their ability to detect movement and trigger alarms or notify authorities provides an additional layer of security for homes, businesses, and other properties. The presence of motion sensors can give homeowners and business owners peace of mind, knowing that their premises are being monitored for any unauthorized activity.
Convenience
In home automation and everyday applications, motion sensors offer unparalleled convenience. Automatic lighting that turns on as you enter a dark room, doors that open when you approach, and other automated functions controlled by motion sensors make daily life easier and more efficient. They eliminate the need for manual operation of switches and devices, especially in situations where your hands might be full or when you are in a hurry.
Monitoring and Safety
In industrial and healthcare settings, motion sensors are essential for monitoring equipment and patient safety. They can detect abnormal movements or vibrations in machinery, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns. In healthcare, they can alert caregivers when a patient has fallen or is in distress, enabling prompt medical attention and potentially saving lives.
What Motion Sensor is Right for Me? https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Consider the Application
The first factor to consider when choosing a motion sensor is the intended application. For simple indoor lighting control in a residential setting, a basic PIR sensor might be sufficient. If you need to monitor a large outdoor area or detect movement through walls, a microwave sensor could be a better choice. For high-security applications where false alarms must be minimized, a dual tech sensor is advisable. In industrial or automation applications that require precise distance measurement along with motion detection, ultrasonic sensors are often the preferred option.
Detection Range and Coverage
Assess the area you need to cover with the motion sensor. Different sensors have varying detection ranges, from a few feet to several dozen feet. Make sure the sensor you choose can cover the desired area effectively. For example, if you want to install a motion sensor to light up a long driveway, you'll need a sensor with a wide detection range.
Environmental Conditions
Take into account the environmental conditions where the sensor will be installed. Some sensors, like PIR sensors, can be affected by extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, which may cause false alarms. Ultrasonic sensors, on the other hand, can work well in various weather conditions. If the sensor will be used in a dusty, humid, or high-temperature environment, choose a sensor that is designed to withstand those conditions to ensure reliable operation.
Power Source
Consider the power source options available for the motion sensor. Some sensors are battery-powered, which offers flexibility in installation but requires periodic battery replacement. Others can be hardwired into the electrical system, providing a continuous power supply but requiring professional installation in some cases. There are also solar-powered motion sensors, which are ideal for outdoor applications where access to electricity is limited.
Cost
Budget is an important consideration. PIR sensors are generally the most affordable, while dual tech and specialized sensors can be more expensive. Evaluate the features and performance you need against the cost to find the best balance. Keep in mind that investing in a higher-quality sensor might be worth it in the long run, especially for critical applications where reliability is crucial.
In conclusion, motion sensors are versatile devices with a wide range of applications and technologies. Understanding their functionality, types, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs can help you harness their benefits effectively, whether it's for enhancing security, saving energy, or improving convenience in your home, business, or other environments.
Motion Sensor IC - SIC Supplier: Your Ideal Partner
In the dynamic electronics landscape, SIC Supplier(https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors) shines as the premier destination for Motion Sensor ICs. Our vast inventory features high - quality ICs from top manufacturers, ensuring reliable performance across various applications. With competitive pricing, swift delivery, and expert technical support, we meet diverse customer needs. Whether for security, automation, or industrial use, trust SIC Supplier for all your Motion Sensor IC requirements
https://www.sic-components.com/motion-sensors
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse












 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)