
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
Understanding Resistors: Basics, Types, Working Principles, and Significance
I. Introduction to Resistors
In the realm of electrical engineering, resistors are fundamental passive components that play a pivotal role in electrical circuits. At its essence, resistance is the property of a material to oppose the flow of electric current. Just as a narrow pipe restricts the flow of water, a resistor impedes the passage of electrons through an electrical circuit. Measured in ohms (Ω), resistance quantifies this opposition. A material with zero resistance would allow current to flow unhindered, while a higher resistance value means more difficulty for the current to traverse.
II. Classification of Resistors
A. Fixed Resistors
Fixed resistors are the most commonly used type. Their resistance value is predetermined during manufacturing and remains constant under normal operating conditions. They come in various packages and power ratings, suitable for a wide range of applications. For example, in a simple LED circuit, a fixed resistor is often employed to limit the current flowing to the LED, preventing it from burning out due to excessive current. These resistors are typically color-coded, with bands on their bodies indicating their resistance values and tolerances.
B. Variable Resistors
Variable resistors, as the name suggests, allow the user to adjust their resistance values. Potentiometers are a common type of variable resistor. They are widely used in applications such as volume controls in audio systems. By turning a knob, the position of a wiper along a resistive track changes, altering the resistance between two terminals. Another type is the rheostat, which is used to control the current in a circuit by varying its resistance. It is often found in dimmer switches for lights.
III. How Do Resistors Work?
Resistors function by converting electrical energy into heat energy. When an electric current passes through a resistor, the electrons collide with the atoms in the resistive material. These collisions impede the flow of electrons and dissipate energy in the form of heat. This process is based on the principle of Ohm's Law.
A. Ohm's Law and Current Limitation
Ohm's Law states that the voltage (V) across a resistor is directly proportional to the current (I) flowing through it and the resistance (R) of the resistor, expressed as V = I × R. Rearranging this formula, we get I = V / R. This means that for a given voltage source, by increasing the resistance value, the current flowing through the resistor (and thus the circuit) can be decreased. For instance, if a 12-volt battery is connected to a 6-ohm resistor, the current flowing through it will be 2 amperes (I = 12V / 6Ω = 2A). If the resistance is increased to 12 ohms, the current drops to 1 ampere.
B. Voltage Drop
Resistors also create a voltage drop across them. In a series circuit, where multiple components are connected one after another, the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor equals the total supply voltage. This property is crucial for ensuring that different components in a circuit receive the appropriate voltage. For example, in a circuit with an LED that requires 2 volts to operate and a power supply of 5 volts, a resistor is used to drop the remaining 3 volts, ensuring the LED functions properly.
IV. Key Roles in Circuits and Specific Application Areas
A. Current Limiting and Component Protection
One of the most critical functions of resistors is current limiting. Delicate electronic components such as integrated circuits, diodes, and LEDs are highly sensitive to excessive current. Resistors act as guardians, ensuring that the current remains within safe limits. In an LED flashlight circuit, a resistor is placed in series with the LED to limit the current, preventing it from burning out. Without this resistor, the high current from the battery could quickly destroy the LED.
B. Voltage Division for Precise Power Delivery
Resistors are used in voltage divider circuits to obtain specific voltage levels from a higher input voltage. This is crucial in applications like analog-to-digital converters, where the input voltage needs to be scaled down to a range that the converter can handle. For example, if a microcontroller's analog input pin can only accept voltages up to 3.3 volts, but the sensor output ranges from 0 to 5 volts, a voltage divider circuit using resistors can be designed to scale the sensor's output voltage appropriately.
C. Signal Conditioning in Electronics
In electronic circuits dealing with signals, resistors play a vital role in signal conditioning. They can be used to adjust the amplitude of a signal. In an audio amplifier circuit, resistors are used to set the gain, determining how much the input audio signal is amplified. Additionally, resistors are used for impedance matching between different components. When connecting a microphone to an amplifier, the impedance of the microphone needs to match the input impedance of the amplifier for maximum signal transfer. Resistors can be used to achieve this matching, ensuring clear and distortion-free sound reproduction.
D. Specific Application Areas
Consumer Electronics: In smartphones, resistors are used in countless circuits, from power management to signal processing. They help regulate the current to different components like the processor, display, and camera, ensuring efficient operation.
Automotive Systems: Modern cars are filled with electronic control units (ECUs). Resistors are used in these ECUs for functions such as sensing engine temperature (where a thermistor, a type of variable resistor, is used), controlling the brightness of dashboard lights, and regulating the current to various sensors.
Renewable Energy Systems: In solar panel installations, resistors are used in the charge controllers to regulate the current flowing from the panels to the batteries. They help prevent overcharging and ensure the batteries are charged efficiently and safely.
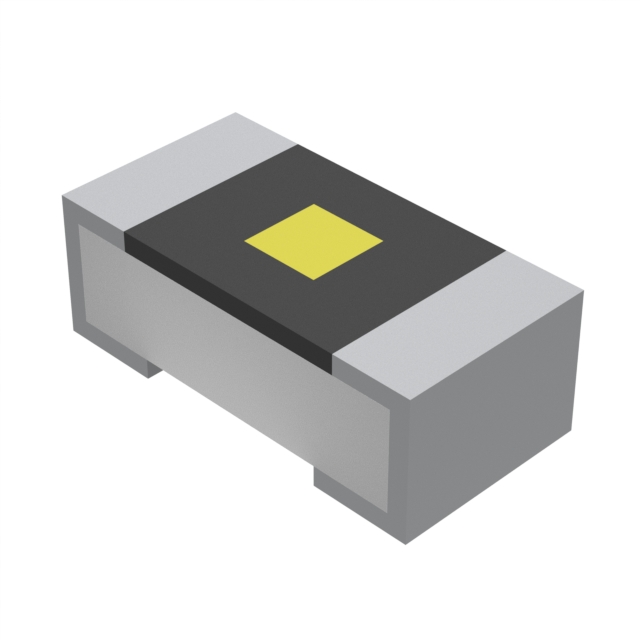
Introducing our chip resistors, the perfect solution for your electronic applications. These compact and versatile components are designed to provide stable and reliable resistance in a wide range of electronic circuits. With their small size and high performance, our chip resistors are ideal for use in telecommunications, automotive, medical, and consumer electronics products. Our chip resistors are manufactured with high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure consistent performance and reliability. They are available in a variety of resistance values and power ratings to meet the specific requirements of your application. Whether you need a standard chip resistor or a custom solution, we can provide the right component for your needs. With their precision construction and durable design, our chip resistors are built to withstand the demands of modern electronic devices. Trust in our chip resistors to deliver exceptional performance and durability in any application.
https://www.sic-components.com/resistors
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse















 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)