
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
Types of acoustic components and piezoelectric acoustic components
In modern electronic devices and acoustic systems, sound components play a crucial role. They convert electrical signals into sound, bringing us various auditory experiences. There is a wide variety of sound components, and different types have unique working principles, characteristics, and application scenarios. Piezoelectric sound components, as an important branch, also have their own unique classifications and features. The following will introduce the types of sound components and piezoelectric sound components in detail.
Types of Sound Components
Mechanical Sound Components
Mechanical sound components produce sound by applying mechanical impact to the sound source. Common application examples include bicycle bells, traditional bells, and gongs. When an external force acts on these components, they vibrate, which in turn causes the surrounding air to vibrate, forming the sound we hear. This type of sound component has a relatively simple structure, but its sound frequency and timbre are limited. It is mainly suitable for scenarios where the requirements for sound quality are not high and the warning function is emphasized.
Electronic Sound Components
Electronic sound components generate sound by applying electrical signals such as voltage and current to make the sound source part vibrate. According to different working principles, they can be further divided into piezoelectric type, electromagnetic type (magnet type), and electro - dynamic type (dynamic type).
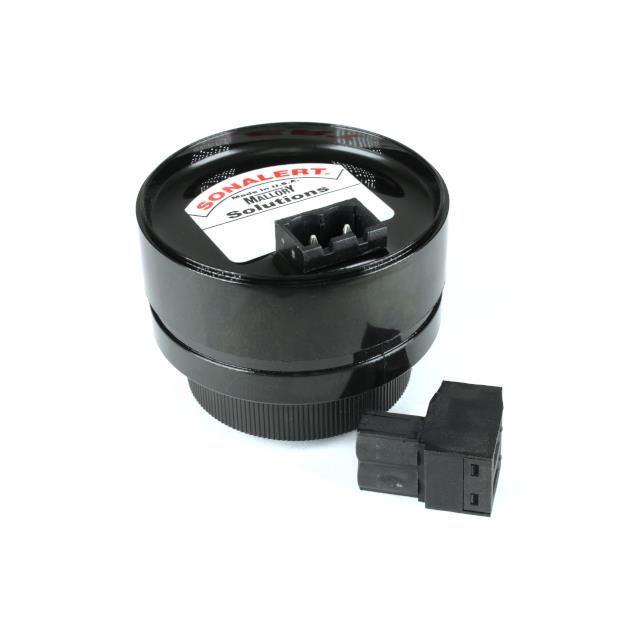
Piezoelectric Type: The piezoelectric - type sound component has a built - in sound - generating element - a piezoelectric vibration plate made by pasting together piezoelectric ceramics and a metal plate, and is usually equipped with a resonator (such as a plastic shell). Its working principle is to input an alternating current signal into the piezoelectric element, causing the piezoelectric vibration plate to vibrate and generate sound. The piezoelectric - type sound component has the remarkable feature of low power consumption (it belongs to the voltage - driven method), which makes it widely used in some devices with high power - consumption requirements. In addition, it has the advantages of being configurable with fewer components, so it is lightweight and easy to be made thin. This is particularly important for electronic products that pursue miniaturization and lightweight, such as in electronic watches, small alarms, and other devices, piezoelectric - type sound components can often be seen.
Electromagnetic Type (Magnet Type): The electromagnetic - type sound component uses a vibrating plate and an electromagnet built in the resonator. When the current in the electromagnet changes, a changing magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field interacts with the magnet, causing the vibrating plate to vibrate and produce sound. However, the electromagnetic - type sound component has high power consumption (it belongs to the current - driven method), which limits its application range to a certain extent. At the same time, because it requires more components to achieve sound production, the overall weight is heavy, and it is difficult to achieve a thin - type design. Despite these disadvantages, in some devices with high requirements for sound intensity and stability, and less sensitive to power consumption and volume, such as specific components of some large - scale audio equipment, the electromagnetic - type sound component still plays an important role.
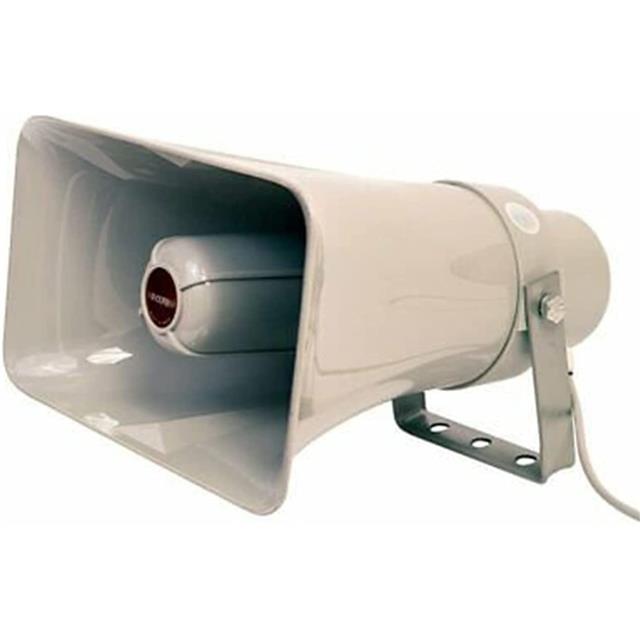
Electro - dynamic Type (Dynamic Type): The working principle of the electro - dynamic type sound component is to use the magnetic field generated by the coil in response to the input signal to make the cone vibrate, thereby producing sound. Compared with the piezoelectric type and the electromagnetic type, the electro - dynamic type sound component has the outstanding feature of being able to obtain distortion - free sound in a wide frequency band, which gives it obvious advantages in high - quality audio - playing devices, such as professional audio systems and high - end headphones. However, as the size of the cone increases, its structure becomes more complex, and the overall product becomes larger and heavier. This may be a disadvantage in some application scenarios with strict restrictions on the volume and weight of the device.
Types of Piezoelectric Sound Components
Piezoelectric Loudspeakers
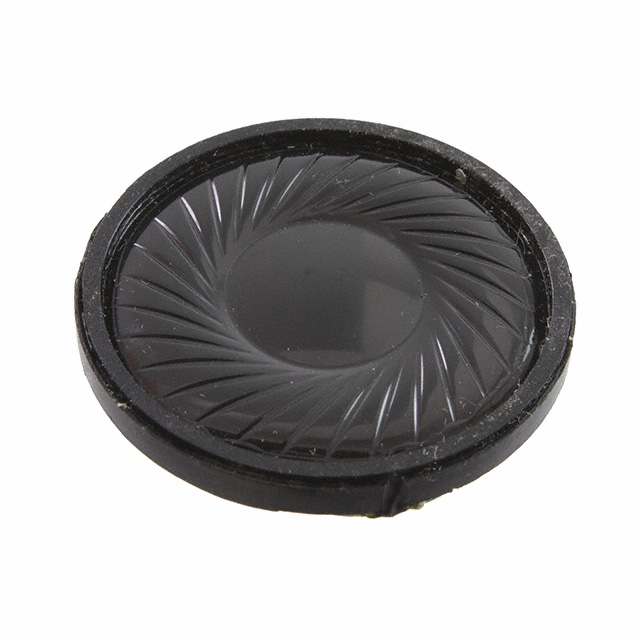
Piezoelectric loudspeakers are composed of a piezoelectric vibration plate combined with a plastic shell (resonator). The piezoelectric vibration plate is its core component, and it has various structural forms. One form is to attach electrodes to both sides of the piezoelectric ceramic, perform polarization treatment, and then bond it to one or both sides of the metal plate. According to different electrode layouts, it can be divided into two types: separately - excited vibration type and self - excited vibration type. When the ceramic is only pasted on one side of the metal plate, it is called a single - layer piezoelectric sheet type, and when it is pasted on both sides of the metal plate, it is called a double - layer piezoelectric sheet type. Piezoelectric loudspeakers do not have a built - in drive circuit. The basic vibrating frequency for producing a loud sound has a nominal value, but it is not limited to this frequency. Instead, it can vibrate freely according to the external input signal conditions, which makes it have application value in some occasions where flexible control of sound frequency and waveform is required, such as in some experimental equipment or specific audio signal processing systems.
Piezoelectric Buzzers
Piezoelectric buzzers have an oscillating circuit built into their plastic shells, which is one of the important differences from piezoelectric loudspeakers. Its most significant feature is that it can produce sound as long as a DC power supply (such as a dry battery) is applied, and the vibrating frequency is fixed. This characteristic makes piezoelectric buzzers widely used in many devices with relatively simple sound requirements, such as simple sound - effect production in electronic toys and fault alarms in some small - scale devices. In principle, when a DC power supply is connected to the oscillating circuit, the oscillating circuit generates an electrical signal of a specific frequency, which drives the piezoelectric vibration plate to vibrate and produce sound. In practical applications, piezoelectric buzzers, with their advantages of simplicity, ease of use, and low cost, have become indispensable sound components in many electronic products.
Buzzers VS. Loudspeakers
Essentially, the key difference between buzzers and loudspeakers is that buzzers have a piezoelectric - type circuit, while loudspeakers do not. Although in general concepts, loudspeakers are usually considered to belong to the category of buzzers, in some professional fields, such as in companies like Murata, they are clearly distinguished. Loudspeakers mainly use external input electrical signals to drive the piezoelectric vibration plate and use the resonator to amplify the sound. The frequency and waveform of its sound can be flexibly changed according to the input signal. On the other hand, because buzzers have a built - in oscillating circuit, they can produce sound by simply connecting to a DC power supply according to the preset frequency. They are relatively less flexible in sound control but are more convenient for applications in simple sound - producing scenarios. In addition, speakers are also important sound - generating components. They use specially designed vibrating plates. Compared with piezoelectric loudspeakers and piezoelectric buzzers, speakers expand the frequency range, can generate a larger sound pressure, and at the same time make the frequency dependence of the sound pressure flatter. They also do not have a built - in drive circuit. If two speakers are used, they can be used as a stereo sound source and are widely used in various audio systems with high requirements for sound quality.
There is a rich variety of sound components and piezoelectric sound components, and each type has its unique performance characteristics and application scenarios. In the actual design of electronic devices and the construction of acoustic systems, it is necessary to reasonably select suitable sound components according to specific requirements, such as power - consumption requirements, sound - quality requirements, and device volume and weight limitations, in order to achieve the best acoustic effect and product performance. With the continuous progress of science and technology, the technology of sound components is also constantly evolving. It is expected that more new - type sound components with excellent performance and unique functions will emerge in the future, bringing more innovation and convenience to our lives and applications in various fields.
If you are interested in the specific application scenarios or future development trends of a certain type of component, we can further expand on the relevant content and provide you with more targeted information.
SIC Electronic offers a wide range of audio electronic components and ICs, aiming to enhance and optimize your audio devices. We provide a wide variety of high - quality components, including amplifiers, speakers, transducers, and signal processors. Our components are carefully designed to deliver excellent sound quality and performance, making them the perfect choice for audio enthusiasts and professionals. With our audio electronic components, you can enjoy clear audio with minimal distortion and powerful bass, providing an immersive listening experience. Whether you are building a home theater system, a recording studio, or upgrading your current audio setup, our components are designed to meet your needs. We are committed to providing reliable and innovative audio solutions that exceed industry standards. Our components are meticulously crafted using top - grade materials and cutting - edge technology to ensure long - lasting durability and stable performance. Experience the difference of our audio electronic components and take your audio system to the next level.
https://www.sic-components.com/integrated-circuits-ics/audio-special-purpose
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse






















 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)