
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
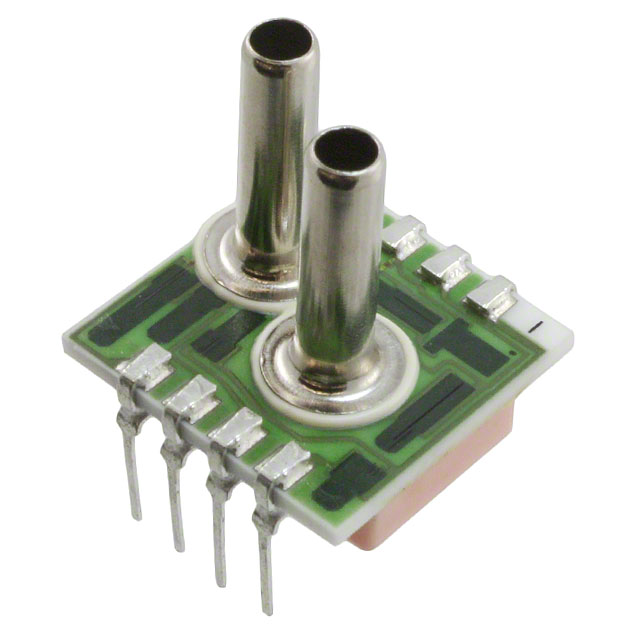
Pressure Sensors
1. What is a Pressure Sensor? https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
A pressure sensor is a device that measures the pressure exerted by gases or liquids, converting mechanical force into an electrical signal for analysis and control. Pressure, defined as force per unit area (P =F/A), is typically measured in Pascals (Pa) or bar. These sensors are critical in industries ranging from automotive to healthcare, enabling real-time monitoring of systems, predictive maintenance, and safety protocols.Unlike simple mechanical gauges, modern pressure sensors offer precision, durability, and compatibility with digital systems. They are often confused with terms like "transducers" (voltage output) or "transmitters" (current output), but all share the core function of translating physical pressure into actionable data.
2. Developments of Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Early Innovations
17th Century: Evangelista Torricelli invented the barometer, laying the foundation for pressure measurement using mercury columns.
19th Century: Eugène Bourdon’s 1849 invention of the Bourdon tube introduced mechanical pressure gauges, widely used in steam engines and industrial machinery.
Modern Technological Leap
Post-1950s: The rise of electronics enabled strain gauge sensors, where resistance changes under pressure.
1980s: Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) revolutionized design, allowing miniaturized, low-power sensors in smartphones and automotive systems.
2000s-Present: Integration with IoT, AI, and wireless technologies (e.g., Bluetooth, 5G) has driven smart, self-calibrating sensors for remote monitoring.
3. How Does a Pressure Sensor Work? https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Pressure sensors operate via transduction mechanisms that convert mechanical deformation into electrical signals:
Sensing Element: A diaphragm, piston, or bourdon tube deforms under pressure.
Transduction:
Piezoelectric: Crystals generate an electric charge proportional to pressure (e.g., engine knock detection).
Capacitive: Pressure bends a diaphragm, altering capacitance between plates (e.g., HVAC airflow sensors).
Strain Gauge: Deformation changes the resistance of a metal foil, measured via Wheatstone bridges (e.g., industrial load cells).
Signal Conditioning: The raw signal is amplified, filtered, and converted to digital data (e.g., 0-5V, 4-20 mA) for processing.
4. Classification of Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
By Measurement Type
Absolute Pressure Sensors: Reference a vacuum (e.g., altitude measurement in aircraft).
Gauge Pressure Sensors: Reference ambient air pressure (e.g., tire pressure monitoring).
Differential Pressure Sensors: Measure the difference between two pressures (e.g., filter clog detection in pipelines).
Vacuum Pressure Sensors: Detect pressures below atmospheric level (e.g., semiconductor manufacturing).
By Technology
Mechanical: Bourdon tubes, aneroid capsules (rugged, low-cost, the slow response).
Electrical:
Strain Gauge: High accuracy for static/dynamic loads.
Piezoelectric: Ideal for high-frequency measurements (e.g., engine combustion).
MEMS: Miniature, low-power (e.g., smartphone accelerometers repurposed for pressure).
Optical/Fiber-Optic: Use light obstruction or phase shifts for harsh environments (e.g., subsea pipelines).
5. Functions of Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Monitoring: Real-time tracking of pressure in systems (e.g., boiler safety, blood pressure devices).
Control: Adjust valves or pumps based on pressure feedback (e.g., automatic tire inflation).
Safety: Trigger alarms or shutdowns during overpressure (e.g., gas pipelines, medical oxygen tanks).
Analytics: Predict maintenance needs via pressure trend analysis (e.g., industrial machinery wear).
6. Applications of Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Industrial
Manufacturing: Monitor hydraulic systems, detect leaks in pipelines, and optimize compressor efficiency.
Energy: Measure pressure in oil wells, steam turbines, and renewable energy systems (e.g., wind turbine hydraulics).
Automotive
Engine Management: Fuel injection pressure, oil pressure, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).
Safety: Airbag deployment via crash-induced pressure spikes.
Healthcare
Ventilators: Regulate air pressure for patient respiration.
Diagnostics: Blood pressure monitors and intraocular pressure sensors for glaucoma.
Aerospace
Cabin Pressure: Maintain safe altitude conditions during flight.
Propulsion: Monitor fuel pressure in rocket engines.
Consumer Electronics
Smartphones: Barometric pressure sensors for altitude tracking in fitness apps.
Home Appliances: Dishwashers and washing machines optimize water pressure.
7. Choosing the Right Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Key Considerations
Pressure Range: Ensure the sensor handles minimum/maximum pressures (e.g., 0-10 bar for HVAC vs. 0-1000 bar for hydraulic systems).
Environment:
Temperature: High-temperature sensors for engines (-40°C to 125°C).
Corrosion: Stainless steel or ceramic sensors for chemical environments.
Accuracy/Resolution: Critical for medical devices (±0.1% FS) vs. industrial use (±1% FS).
Output Type: Analog (voltage/current) for simplicity or digital (CAN, RS-485) for complex systems.
Sensor Selection Flowchart
Determine measurement type (absolute/gauge/differential).
Identify environmental constraints (temperature, moisture, EMI).
Choose technology based on precision and response time needs.
Ensure compatibility with data acquisition systems.
8. Future of Pressure Sensors https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
IoT and Edge Computing: Self-powered, wireless sensors for remote monitoring (e.g., smart cities, predictive maintenance).
AI Integration: Machine learning to predict sensor failure and optimize performance (e.g., predictive analytics for pipelines).
Nanotechnology: Ultra-sensitive nanoscale sensors for biomedical applications (e.g., in-vivo pressure monitoring).
Sustainability: Energy harvesting (e.g., piezoelectric sensors converting mechanical energy to power).
Multifunctional Designs: Combined pressure-temperature sensors reducing system complexity.
9. Pressure Sensors: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers
Q: Can pressure sensors measure both liquids and gases?
A: Yes, but viscous fluids (e.g., oil, pulp) may require specialized diaphragms.
Q: How often should pressure sensors be calibrated?
A: Annually for industrial applications, or as per manufacturer guidelines (e.g., medical devices may require quarterly checks).
Q: What’s the difference between a pressure sensor and a pressure switch?
A: A sensor measures continuous pressure, while a switch triggers an action at a set threshold (e.g., pump activation).
Q: Are MEMS sensors reliable for high-pressure applications?
A: MEMS are ideal for low-to-medium pressure (e.g., 0-100 bar). High-pressure applications (e.g., 1000+ bar) require robust designs like strain gauge or piezoelectric sensors.
Pressure sensors are indispensable in modern technology, bridging physical phenomena with digital intelligence. From the humble Bourdon tube to cutting-edge MEMS devices, their evolution has driven advancements in safety, efficiency, and innovation. As a global leader in sensing technology, SIC Company delivers cutting-edge pressure sensors tailored to diverse industrial and consumer needs. Our extensive portfolio includes piezoelectric, MEMS, strain gauge, and differential pressure sensors, sourced from top manufacturers to ensure reliability and accuracy. Whether you need rugged sensors for high-pressure industrial pipelines or compact MEMS solutions for smart devices, SIC offers unmatched versatility.
Why Choose SIC?
Quality Assurance: All sensors undergo rigorous testing for durability, precision, and environmental resistance, meeting ISO, API, and industry-specific standards.
Global Reach: With streamlined logistics and localized support, we ensure rapid delivery and responsive service worldwide, minimizing downtime for your operations.
Applications We Serve:
Industrial automation, automotive, healthcare, aerospace, and smart infrastructure.
From hydraulic systems to ventilators, our sensors empower safety, efficiency, and innovation.
Partner with SIC Company to unlock the full potential of pressure sensing. Contact us today to explore our products and leverage our expertise for your next project. Experience precision that drives progress – only with SIC.
https://www.sic-components.com/pressure-sensors-transducers

Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse

















 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)