The LM2596, a widely used step-down switching voltage regulator introduced by Texas Instruments, performs prominently in the field of power management. This article will explore its core characteristics, working principles, and practical applications.
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Overview
The LM2596 series voltage regulators are monolithic integrated circuits that provide all active functions for step-down (buck) switching regulators. They can drive 3A loads with excellent line and load regulation capabilities. This series of devices includes versions with fixed output voltages of 3.3V, 5V, and 12V, as well as an adjustable output version to meet different application requirements.
It operates at a switching frequency of 150kHz, which allows the use of smaller-sized filtering components compared to lower-frequency switching regulators. It adopts the standard 5-pin TO-220 package (with various lead bending options) and 5-pin TO-263 surface-mount package, making it easy to use. Only a few external components are required for operation, and it contains internal frequency compensation and a fixed-frequency oscillator.
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Pinouts
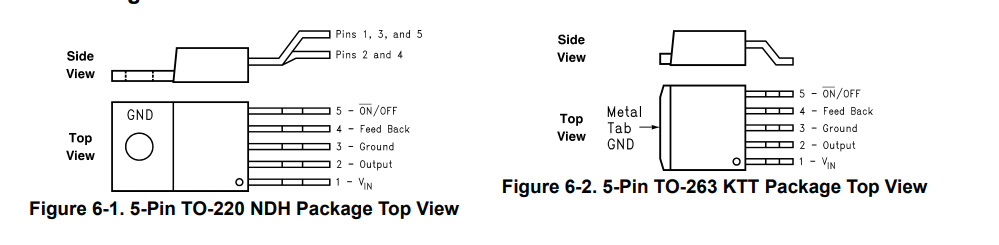
| PIN NO. | PIN NAME | I/O | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | I | This is the positive input supply for the IC switching regulator. A suitable input bypass capacitor must be present at this pin to minimize voltage transients and to supply the switching currents required by the regulator. |
| 2 | Output | O | Internal switch. The voltage at this pin switches between approximately (+VIN−VSAT) and approximately - 0.5 V, with a duty cycle of VOUT/VIN. To minimize coupling to sensitive circuitry, the PCB copper area connected to this pin must be kept to a minimum. |
| 3 | Ground | — | Circuit ground |
| 4 | Feedback | I | Senses the regulated output voltage to complete the feedback loop. |
| 5 | ON/OFF | I | Allows the switching regulator circuit to be shut down using logic signals thus dropping the total input supply current to approximately 80 μA. Pulling this pin below a threshold voltage of approximately 1.3 V turns the regulator on, and pulling this pin above 1.3 V (up to a maximum of 25 V) shuts the regulator down. If this shutdown feature is not required, the ON/OFF pin can be wired to the ground pin or it can be left open. In either case, the regulator will be in the ON condition. |
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Specifications
| Type | Range |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage | 37V |
| Maximum Output Current | 3A |
| Input Voltage Name | 12V |
| Minimum Supply Voltage | 4.5V |
| Nominal Quiescent Current | 5mA |
| Maximum Output Voltage | 37V |
| Maximum Duty Cycle | 95% |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C ~ 125°C TJ |
| Operating Supply Voltage | 40V |
| Maximum Supply Voltage | 40V |
| Voltage - Output (Minimum/Fixed) | 1.23V |
| Control Mode | Voltage Mode |
| Halogen-Free | Yes |
| Minimum Output Voltage | 1.23V |
| Maximum Junction Temperature (TJ) | 125°C |
What is the PWM control principle of the LM2596 voltage regulator?
The LM2596 uses pulse-width modulation (PWM) to regulate output voltage. Its internal oscillator generates a 150kHz fixed-frequency clock. The error amplifier compares the feedback voltage (from the output via voltage dividers) with a reference voltage, producing an error signal. This signal controls the PWM comparator, which adjusts the duty cycle of the internal power switch (MOSFET/BJT).
When the switch is on, input voltage supplies energy to the inductor and load; when off, the inductor discharges through the freewheeling diode, maintaining current. By varying the on-time proportion (duty cycle), the average output voltage is regulated. Higher duty cycles increase output voltage, while lower ones decrease it, ensuring stable output despite input or load changes.
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Features
Output voltage options: Fixed output voltage versions providing 3.3V, 5V, and 12V, as well as an adjustable version with an output voltage range of 1.2V to 37V.
Accuracy: The maximum error is ±4% under the entire line and load conditions.
Load capacity: Can provide an output load current of 3A.
Input voltage range: Up to 40V.
External component requirements: Only four external components are needed, making it easy to use.
Switching frequency: The internal oscillator has a fixed frequency of 150kHz.
Shutdown function: Has TTL shutdown capability, and the quiescent current IQ in low-power standby mode is typically 80μA.
Efficiency: High efficiency, with different versions having different efficiencies under specific conditions. For example, the 12V version has a typical efficiency of 90% when the input voltage is 25V and the load current is 3A.
Protection features: Equipped with thermal shutdown and current limiting protection functions to ensure the safety of the device under fault conditions.
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Applications
The LM2596, as a high-performance step-down switching regulator, is widely used in various electronic systems due to its advantages such as high efficiency, strong load capacity, and flexible output voltage options. Its typical applications include:
Industrial Control Systems: It provides stable power supply for sensors, actuators, and control circuits in industrial environments. With a maximum input voltage of 40V, it can adapt to unstable industrial power grids, ensuring reliable operation of equipment.
Automotive Electronics: Suitable for in-vehicle devices like car audio, navigation systems, and on-board chargers. Its 3A load capacity meets the power requirements of most automotive electronic components, and the thermal shutdown and current limit protection functions enhance safety during vehicle operation.
Telecommunications Equipment: Used in routers, modems, and communication modules to convert high-voltage inputs (such as 12V or 24V) to the low-voltage (3.3V, 5V, etc.) required by core chips, ensuring stable signal transmission.
Battery-Powered Devices: The adjustable output version (1.2V to 37V) is ideal for devices powered by batteries (like lead-acid batteries or lithium-ion batteries), enabling flexible voltage regulation to extend battery life.
Power Supplies for Embedded Systems: Provides stable power for microcontrollers (e.g., STM32 series), FPGAs, and other embedded components. Its low standby current (typical 80μA) helps reduce power consumption in low-power modes.
LED Lighting Systems: Can drive high-power LED arrays by adjusting the output voltage to match the working voltage of LEDs, with high efficiency reducing heat generation and improving system stability.
LM2596 Fixed Voltage Regulator
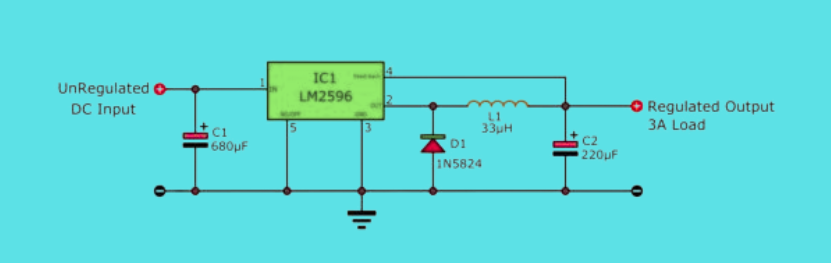
Fixed voltage regulator versions. Refer to the circuit above. We can set the output voltage by changing the IC:
- LM2596-3.3 for 3.3V output.
- LM2596-5.0 for 5V output.
- LM2596-12 for 12V output.
We should also have other appropriate components:
- C1 should be 330uF (when using LM2596-3.3, LM2596-5.0) or 180uF (for LM2596-12).
- L1 = coil inductance, with a value of 33uH (for LM2596-3.3, LM2596-5.0) or 68uH (for LM2596-12).
LM2596 Adjustable Output Voltage Regulator
Now we see that most people use the LM2596 as an adjustable output voltage regulator.
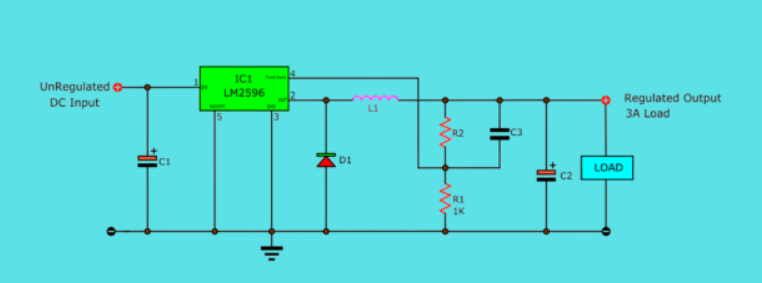
The LM2596 adjustable output voltage regulator, as shown, uses IC1 (LM2596), with C1 filtering input. L1, D1, R1, R2, C2, C3 form the circuit. It takes unregulated DC input, adjusts via feedback (R1/R2), outputs regulated voltage for 3A loads, enabling flexible voltage regulation.
LM2596 Voltage Regulator Alternatives
LM2596 is a popular step-down switching regulator, but there are several alternatives available that offer similar or enhanced performance for different applications. Here are some common alternatives:
1. LM2576
A predecessor to the LM2596, offering similar functionality with a maximum output current of 3A.
Operates at a lower switching frequency (52kHz) compared to LM2596 (150kHz), which may require larger external components.
Available in fixed voltage versions (3.3V, 5V, 12V) and adjustable versions.
A compact, high-efficiency step-down converter with a maximum output current of 3A.
Features a higher switching frequency (up to 1.2MHz), allowing for smaller inductors and capacitors.
Offers better efficiency than LM2596 in many operating conditions, making it suitable for battery-powered devices.
3. XL4015
A high-current step-down regulator capable of delivering up to 5A of output current, making it ideal for higher power applications.
Has an adjustable output voltage range from 1.25V to 36V.
Includes over-current and over-temperature protection features.
A linear regulator, unlike the switching regulators mentioned above, which makes it simpler but less efficient for large voltage drops.
Available in fixed voltage (1.8V, 2.5V, 3.3V, 5V) and adjustable versions with a maximum output current of 800mA.
Produces less noise than switching regulators, making it suitable for sensitive analog circuits.
5. TPS5430
A 3A step-down converter with a wide input voltage range (5V to 36V) and adjustable output voltage (1.22V to 28V).
Features high efficiency (up to 95%) and a switching frequency of 500kHz.
Includes built-in protection functions such as over-current, over-voltage, and thermal shutdown.
Functions of LM2596
Voltage conversion: It can convert an unregulated higher DC input voltage into a stable lower DC output voltage. It offers both fixed output voltage versions (such as 3.3V, 5V, 12V) and an adjustable version whose output voltage can be set within the range of 1.2V to 37V.
Driving capability: It is capable of driving a maximum load current of 3A, making it suitable for powering various electronic devices with moderate current requirements.
Efficiency optimization: Operating at a fixed switching frequency of 150kHz, it allows the use of smaller-sized filtering components compared to lower-frequency regulators, while achieving good efficiency in voltage conversion.
Protection features: It incorporates thermal shutdown and current-limiting protection functions. The thermal shutdown protects the device from damage due to excessive temperature, and the current limiting prevents excessive current from flowing through the regulator, safeguarding both the regulator itself and the connected load.
External shutdown control: It has an external shutdown (ON/OFF) function. When this function is activated, the regulator enters a low-current standby mode, reducing power consumption.
Stable output: It provides excellent line and load regulation, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable even when there are changes in the input voltage or the load.
LM2596 PCB Layout Guide
Component Layout:
Input capacitor: Place it close to the input pin of the LM2596. A 470μF electrolytic capacitor is often used to reduce input voltage fluctuations.
Output pin: This pin outputs a PWM wave of approximately 150kHz during normal operation, and main peripheral components are connected here. When laying out, it is necessary to consider the convenience of connection with related components and signal integrity.
Ground pin: The ground pin should be short and thick to ensure good grounding, and can be connected to the ground layer through multiple vias.
Feedback pin: The feedback pin is connected to the feedback resistor, and should be as close to the chip as possible with short traces to reduce interference and ensure the accuracy of the output voltage.
Control pin: The control pin is grounded or connected to a high level according to the working mode. During layout, the convenience of connection with the control signal source should be considered.
Overall layout: Arrange high-speed devices (such as the LM2596 itself) close to each other to shorten the length of high-speed signal lines. At the same time, separate analog, digital, and high-speed signals into different areas to avoid mutual interference. Power devices should be evenly distributed, and heat dissipation space should be reserved to facilitate air flow for heat dissipation.
Trace Design:
Try to avoid long-distance parallel traces, especially for power lines and signal lines, to prevent crosstalk.
Input and output power lines should be thick enough to meet the requirements of large current transmission, reduce line resistance and voltage drop, and copper pouring can be used if necessary.
Grounding Treatment:
Design separate analog ground and digital ground, and finally connect them at a single point to avoid ground loop interference.
Multi-layer PCBs can be used, with the middle layer as the ground layer to enhance grounding effect and reduce electromagnetic interference.
Other Aspects:
If conditions permit, use multi-layer PCBs, with the middle layer as the ground layer or power layer to shield and reduce crosstalk.
Utilize 3D package libraries to visualize components during the design stage, ensuring reasonable layout, avoiding installation problems, and achieving a compact layout that meets electrical and mechanical requirements.
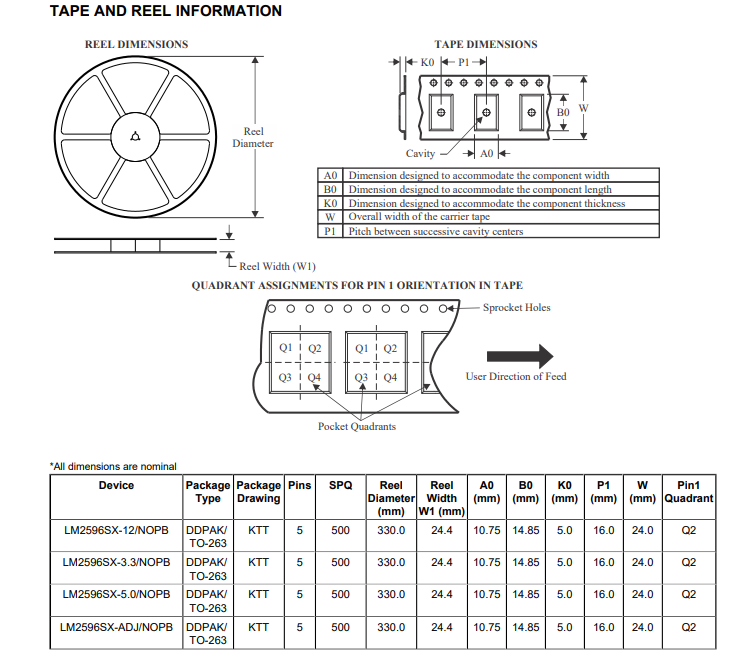
LM2596 Series Models
| Part number | Status | Package | Pins | Carrier | RoHS | MSL rating | Op temp (°C) | Part marking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM2596S-12/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | - | LM2596S-12 P+ |
| LM2596S-12/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-12 P+ |
| LM2596S-3.3/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | - | LM2596S-3.3 P+ |
| LM2596S-3.3/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-3.3 P+ |
| LM2596S-5.0/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | - | LM2596S-5.0 P+ |
| LM2596S-5.0/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-5.0 P+ |
| LM2596S-ADJ/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-ADJ P+ |
| LM2596S-ADJ/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | TUBE | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-ADJ P+ |
| LM2596SX-12/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | LARGE T&R | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | - | LM2596S-12 P+ |
| LM2596SX-12/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | LARGE T&R | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | -40 to 125 | LM2596S-12 P+ |
| LM2596SX-3.3/NOPB | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 | LARGE T&R | ROHS Exempt SN | Level-3-245C-168 HR | - | LM2596S-3.3 P+ |
| LM2596SX-3.3/NOPB.B | Active Production | DDPAK/TO-263 (KTT) | 5 |
LM2596 Package
To sum up, the LM2596 voltage regulator occupies an important position in the electronics field due to its excellent performance, simple operation, and wide range of applications. Meanwhile, its alternative products also provide more options for designs with different requirements.









 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items) 